513.找树左下角的值
难度:中等
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
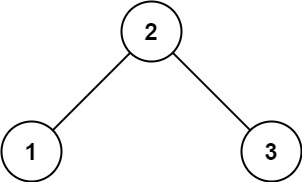
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1示例 2:
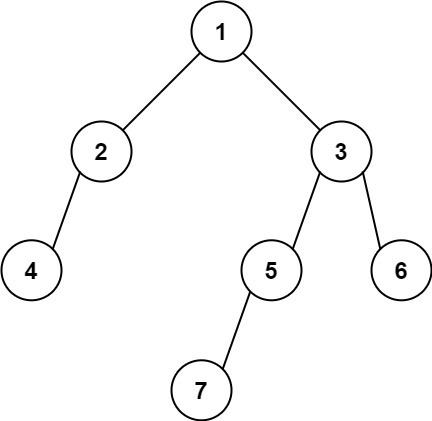
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[1,10^4] -2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
层序遍历+队列法
联想 199.二叉树的右视图 题,可以知道这个题最容易想到的做法就是直接层序遍历,遍历到最后一层的时候,把最后一层的第一个节点输出即可。
代码展示
java
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
int result = 0;
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 根节点入队
queue.add(root);
// BFS 循环
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentLayerSize = queue.size();
// 这里一定要使用固定大小currentLayerSize,不要使用queue.size(),因为queue不停地出队入队,所以其大小是不断变化的
for (int i = 0; i < currentLayerSize; i++) {
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
// 记录每一行的第一个元素
if (i == 0) {
result = current.val;
}
if (current.left != null) {
queue.add(current.left);
}
if (current.right != null) {
queue.add(current.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次。
空间复杂度:O(n),最差情况下,即当树为满二叉树时,最多有 (n+1)/2 个树节点 同时 在 queue 中,故使用 O(n) 大小的额外空间。
总结
二叉树的层序遍历的队列迭代法需要牢记。
